From:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/YNJBveQ
真正了解qmake的使用方法,直接在终端下输入命令:qmake -help就可以了,帮助内容如下:
Usage: qmake [mode] [options] [files]
QMake has two modes, one mode
for generating project files based on
some heuristics, and the
other for generating makefiles. Normally you
shouldn't need to specify a mode, as makefile generation is the default
mode for qmake, but you
may use this to test qmake on an existing project
Mode:
-project Put qmake into project file generation mode
In this mode qmake interprets files as files to
be built,
defaults to *.c; *.ui;
*.y; *.l; *.ts; *.xlf; *.qrc; *.h; *.hpp; *.hh; *.hxx; *.H; *.cpp; *.cc; *.cxx; *.C
Note: The created .pro file probably will
need to be edited. For example add the QT
variable to
specify what modules are required.
-makefile Put qmake into makefile generation
mode (default)
In this mode qmake interprets files as project
files to
be processed, if skipped qmake
will try to find a project
file in your current working directory
Warnings Options:
-Wnone
Turn off all warnings; specific ones may be re-enabled by
later -W options
-Wall Turn on all warnings
-Wparser Turn on
parser warnings
-Wlogic Turn
on logic warnings (on by default)
-Wdeprecated Turn on deprecation warnings (on by
default)
Options:
* You can place any
variable assignment in options and it will be *
* processed as if it was
in [files]. These assignments will be parsed *
*
before
[files].
*
-o file
Write output to file
-d
Increase debug level
-t templ Overrides
TEMPLATE as templ
-tp
prefix Overrides
TEMPLATE so that prefix is prefixed into the value
-help
This help
-v
Version information
-after
All variable assignments after this will be
parsed after [files]
-norecursive Don't do a
recursive search
-recursive Do a recursive search
-set <prop> <value> Set
persistent property
-unset <prop> Unset
persistent property
-query <prop> Query
persistent property. Show all if <prop> is empty.
-cache file Use file as cache
[makefile mode only]
-spec spec Use spec as QMAKESPEC
[makefile mode only]
-nocache Don't use a cache file [makefile mode only]
-nodepend Don't generate dependencies [makefile
mode only]
-nomoc
Don't generate moc targets [makefile
mode only]
-nopwd
Don't look for files in pwd
[project mode only]
qmake命令格式
qmake
[mode] [options] [files]
mode选项
-project 生成.pro文件
-makefile 生成Makefile文件
options选项
-o file 输出文件名,比如qmake -project hello.cpp -o
hello.pro,就会生成一个hello.pro文件,如果是qmake -project
hello.cpp -o hello11.pro,就会生成一个hello11.pro文件
实验1
1、编写代码,命名为hello.cpp,如下
![]()
hello.cpp代码如下
#include<qapplication.h>
#include<qpushbutton.h>
int main(int
argc,char
*argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc,argv);
QPushButton hellobtn("Hello World!",0);
hellobtn.resize(200,50);
hellobtn.show();
return a.exec();
}
2、 qmake -project (用于创建.pro文件,将所有的文件编译成一个与平台无关的工程文件)
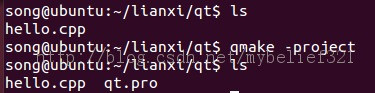
可见默认生成的文件名为 qt.pro
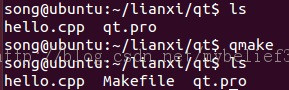
3、 qmake (读取本身的Qt设置,生成与库一致的相应的Makefile)
4、 make
(根据生成的Makefile,将文件编译为二进制可执行程序)
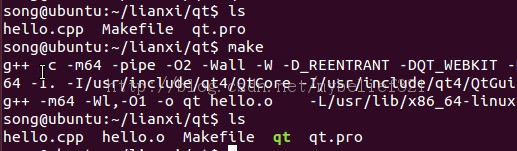
可见生成了qt可执行程序
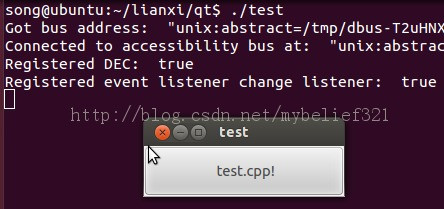
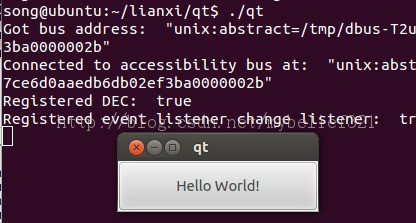
5、执行命令: ./qt
实验2
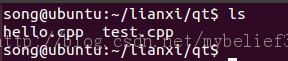
本实验中并没有用到上面所讲的方式,而是直接使用了默认值,但是假设说该文件夹下有两个cpp文件,如下图
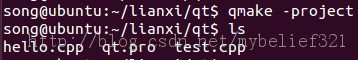
这时候再执行命令:qmake -project会怎么样呢?会出现下面的结果
有点意思,竟然不出错,但是你知道它生成的qt.pro是哪个cpp文件的吗?我不知道,加入这里我想对test.cpp操作,这时候就要按照上面的格式了。
1、qmake -project test.cpp -o test.pro
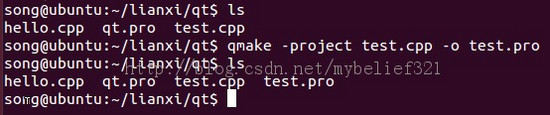
这时候生成了test.pro
2、qmake -makefile test.pro,这里生成test.pro的Makefile
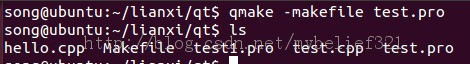
3、make
4、执行命令 ./test