从端口传输
1、信号signal
从端口传输信号角色(signal roles)见Avalon Interface Specification 中的3.2 Avalon Memory-Mapped Interface Signal Roles。
|
信号名 |
||
| address | ||
| readdata | ||
| writedata | ||
| chipselect | ||
| read | ||
| write | ||
| byteenable | ||
| writebyteenable | ||
| begintransfer | ||
2、属性properties
3、时序timing
●从端口读
从端口读传输由Avalon交换架构发起,从Avalon从端口传输一个数据单元(外设的数据端口全宽度)到Avalon交换架构。
◇从端口基本读传输
◇具有一个等待周期的从端口读传输
◇具有可变等待周期的从端口读传输
●从端口写
从端口写传输由Avalon交换架构发起,并由Avalon交换架构到从端口传输一个数据单元(外设的数据端口全宽度)。如果writedata的宽度大于一个字节,使用byteenable来实现对writedata内的特定字节进行写操作。如果从端口没有使用byteenable,则所有的字节段在传输期间都是使能的。
◇从端口基本写传输
◇具有固定等待周期的从端口写传输
◇具有可变等待周期的从端口写传输
◇具有建立和保持时间的从端口写传输
&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&
从端口读
●从端口基本读传输

●具有一个等待周期的从端口读传输

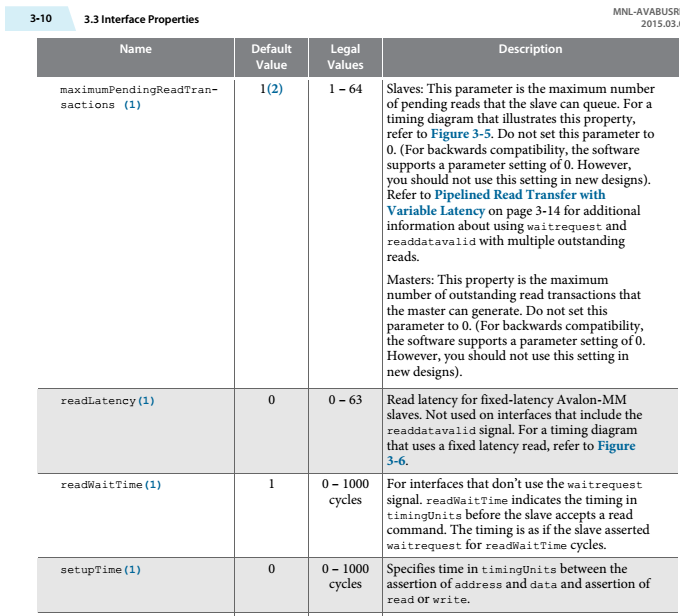
如何设置等待一个周期?
(以下信息来自Avalon Interface Specification)
A slave can specify fixed wait-states using the readWaitTime and writeWaitTime properties. Using fixed wait-states is an alternative to using waitrequest to stall a transfer. The address and control signals (byteenable, read, and write) are held constant for the duration of the transfer. Setting readWaitTime or writeWaitTime to <n> is equivalent to asserting waitrequest for <n> cycles per transfer. In the following figure, the slave has a writeWaitTime = 2 and readWaitTime = 1.
readWaitTime property:
●具有可变等待周期的从端口读传输
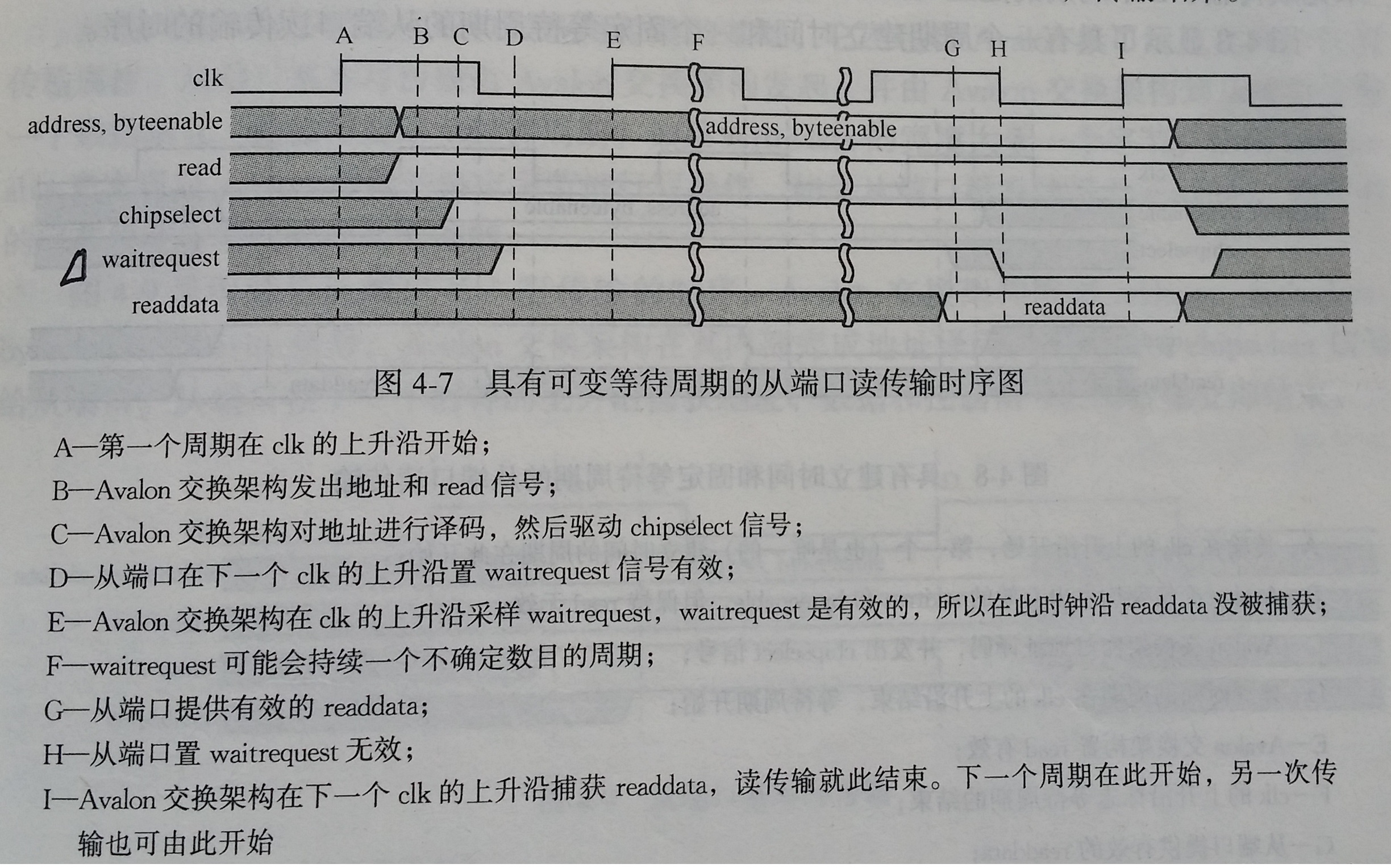
waitrequest definition:
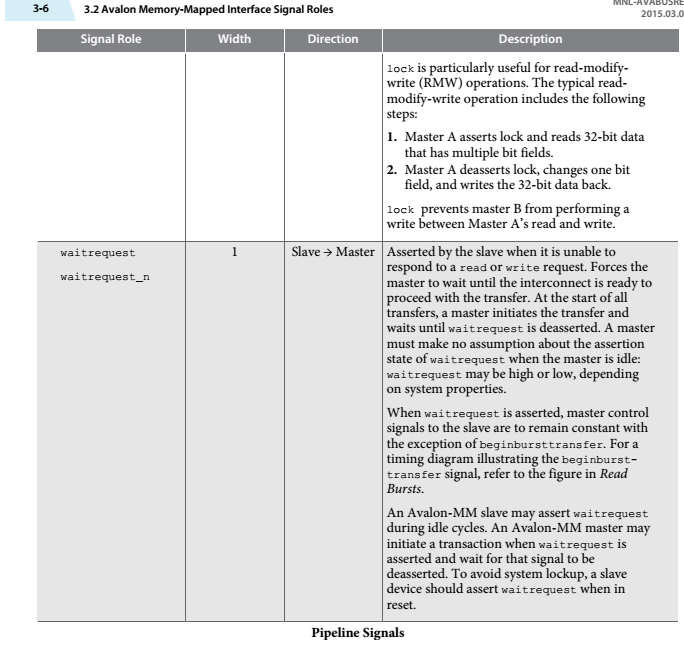
●
从端口写传输
●从端口基本写传输
●具有固定等待周期的从端口写传输
●具有可变等待周期的从端口写传输
●具有建立和保持时间的从端口写传输

holdtime definition: